No one can go back and change their start; but everyone can start now and change their finish.
When a family decides to have a child, everyone imagines how beautiful, intelligent, and happy it will be. Hardly anyone imagines the baby’s future as sick, helpless and unhappy one. Unfortunately, life has not only pleasant surprises. The joy of birth can be clouded by disease message. Among the causes of child disability the nervous disorders are leading, 75% of which occurs during fetal development stage or during childbirth.
The main causes nervous disorders among newborns and children of the first years of life are:
- asphyxiation and hypoxic nervous system damage in children, whose mothers suffered from various acute and chronic diseases during pregnancy;
- infectious nervous system lesions in fetus and newborn, born by women with infectious pathology during pregnancy and childbirth;
- congenital and hereditary diseases of newborns.
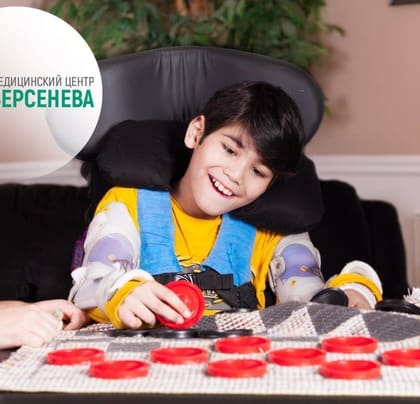
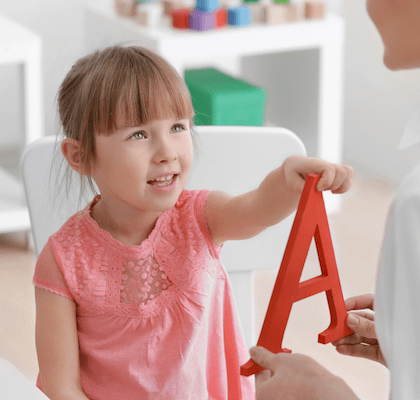
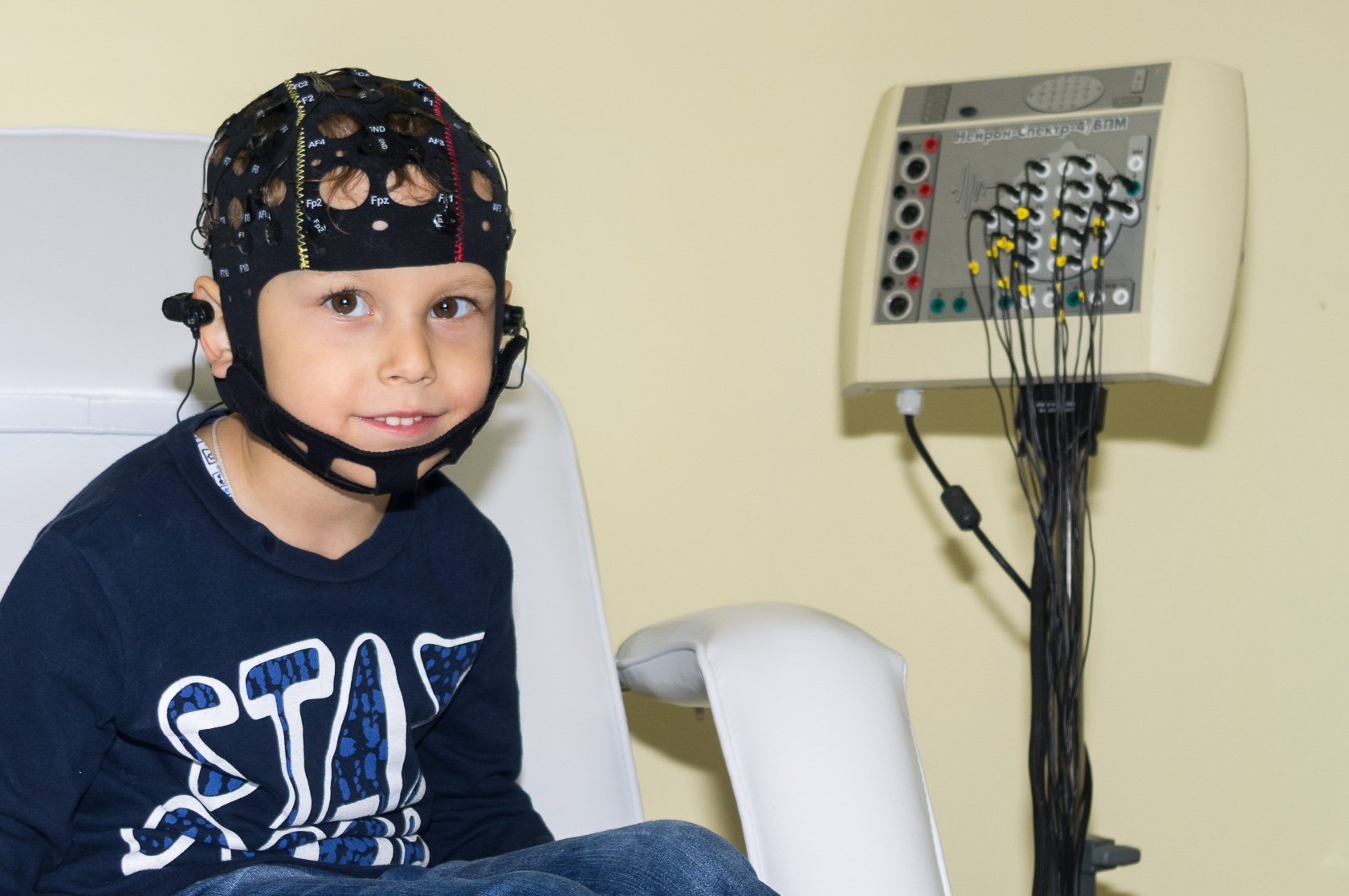
A significant part of the failures to restore the child’s health with nervous system damage is due to late diagnostics and late-onset treatment. The early diagnostics is the key to success in restoring the damaged nervous system. The early diagnostics makes it possible to take advantage especially favourable central nervous system property of newborns – high brain tissue neuroplasticity.
Early therapeutic intervention allows minimizing the source of damage and preventing the occurrence of subsequent severe motor and intellectual disorders. The recovery capabilities of the damaged nervous system are particularly high in the first year of life.
In the process of child’s growth and development against the background of genetic features and under the influence of a number of external factors (lifestyle, eating habits, traumas, diseases), diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system may also occur.
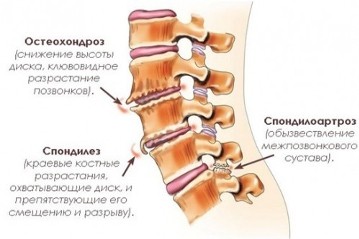
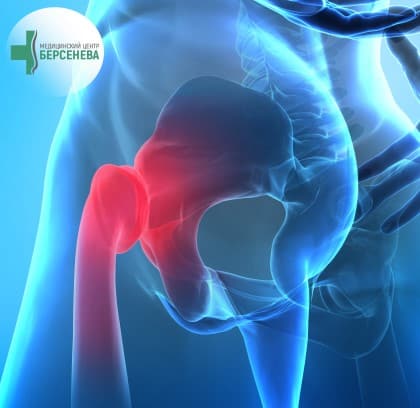
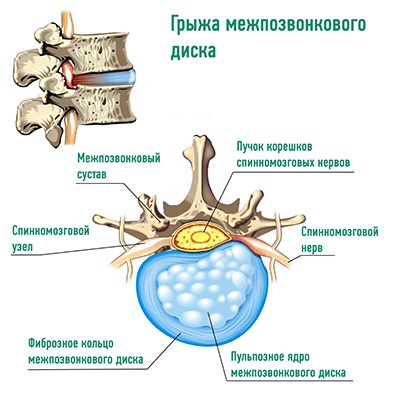
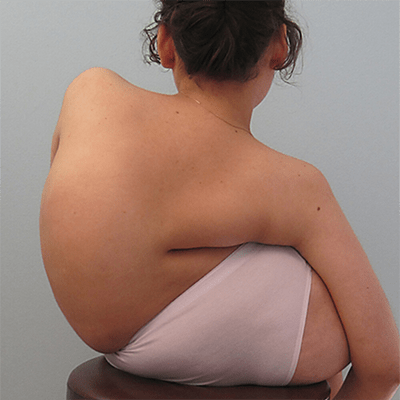
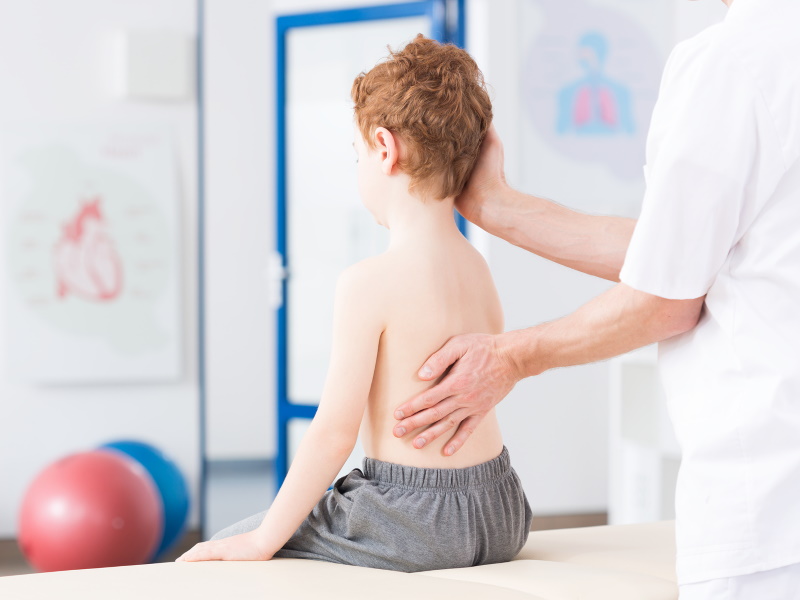
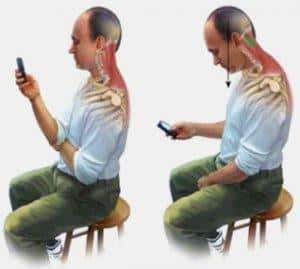
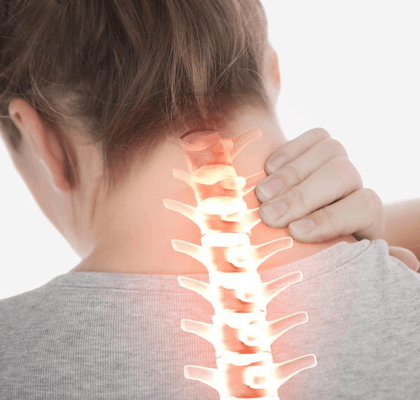
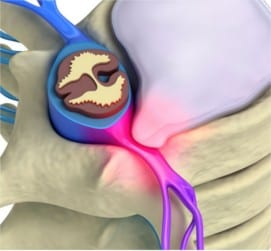
In recent years, more and more children and adolescents have back pain, and the diagnosis confirms that these pains are often caused by posture disorders, scoliotic disease, and degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs. Moreover, the disease can quickly progress, and, as a result, the intervertebral hernia develops in some patients already in adolescence.
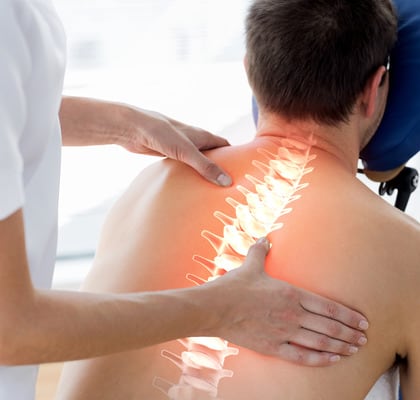
The therapeutic strategy and tactics are reduced to the early prescribing of the pathogenically appropriate complex therapy in a certain set and sequence.
In therapy the preference is given to the use of medicine with high biological activity, the main task of which is to facilitate the restoration of structure and function of the affected nerve cells and structures, while using the enormous regenerative reserves of the growing organism.
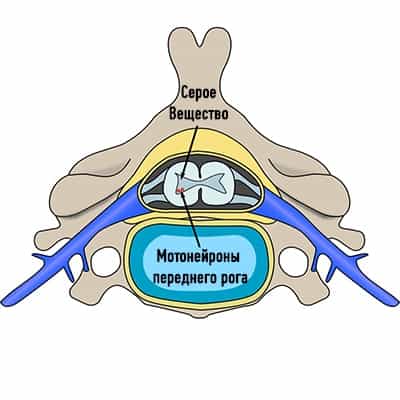
Metameric treatment methods used in our clinic include:
- metameric administration of medicinal preparations (microdose injections into certain zones depending on damage degree);
- metameric acupressure;
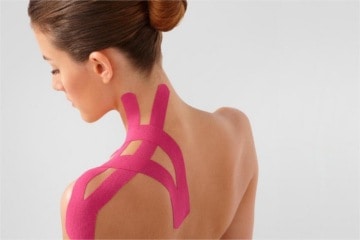
- metameric taping.