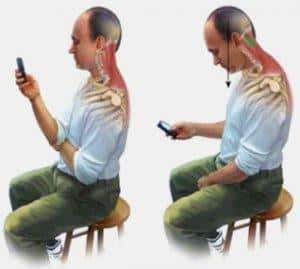
Metamery is a type of animals’ body structure which is characterized by the successive arrangement of the identical, similar to each other segments (metamers). Metamery is a biological regularity; it is typical for all vertebrates and the vast majority of the invertebrates. The greater part of representatives of the living world has retained this property to the present day. Moreover, the more primitive the organism is, the clearer the similarity of contiguous areas is in evidence.
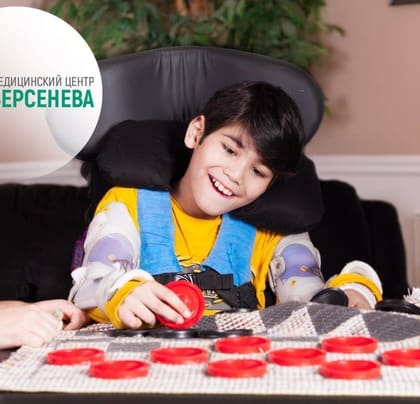
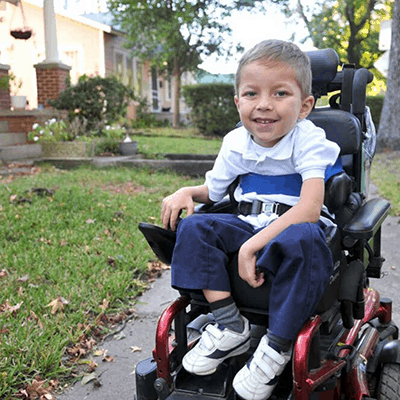
The human body consists of 33 metamers.
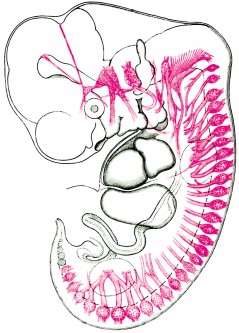
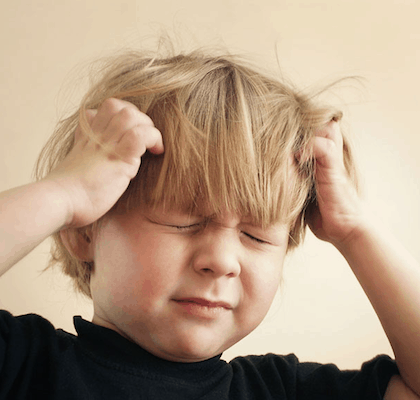
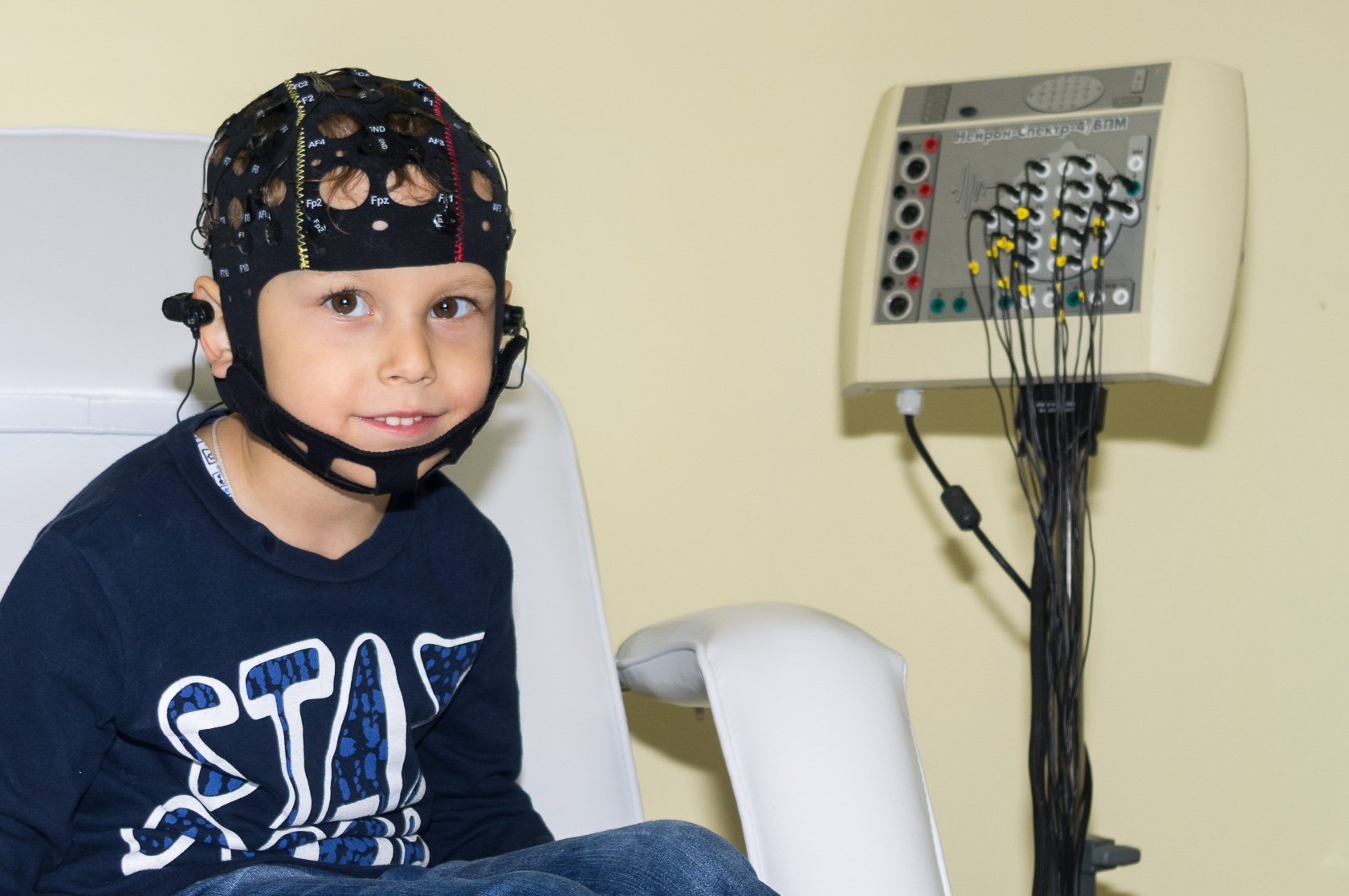
The structure of the cerebrospinal nervous system of the human embryo. The 32nd day of embryonic development, length – 10.2 mm. (Toldt, 1934, page 912).
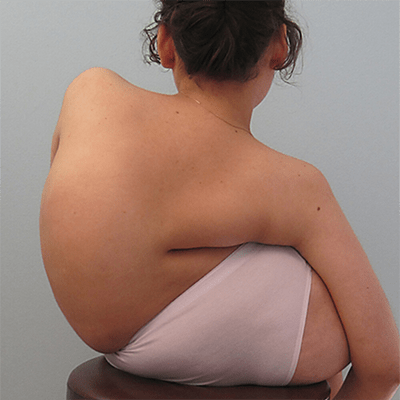
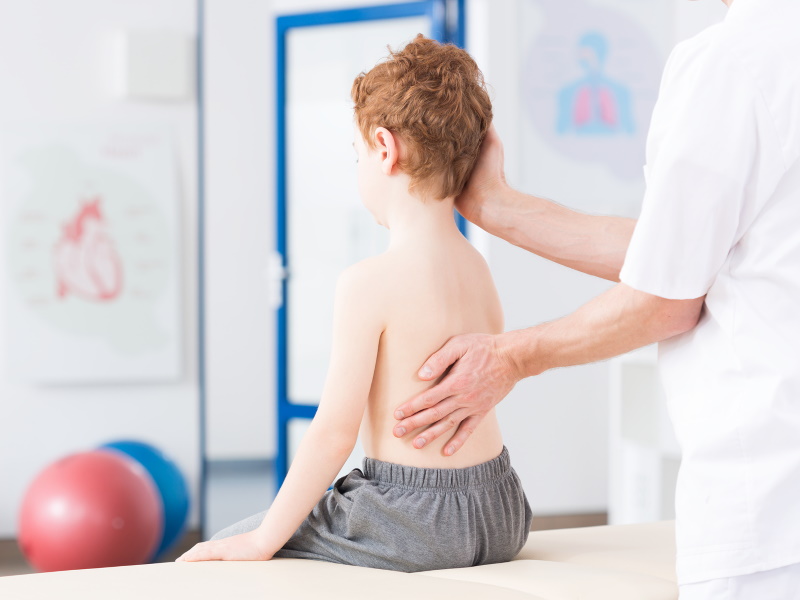
In the evolutionary process the human body received a pseudo-metameric structure. Only in the early embryonic stages the formation of metamers can be traced. Each metamer retains some autonomy and is independently responsible for the coherence of the actions of all seven structures located on its territory – skin, muscles, bones, vessels, internal organs, immune, endocrine and nervous systems. Some metamers have changed – in the process of evolution appeared upper and lower limbs and the three upper metamers merged together and formed the head. But the innervation of organs, which originally belonged to one or another metamer, remained unchanged. Whosesoever the organ was displaced, the nervous system, that provides one or another metamer, fixes on a neuromere (a part of the nervous system), which has “soaked up” a segment of the spinal cord along with nerve roots, spinal ganglia and nerves. That is why the heart or diaphragm, which is displaced for a lot of centimeters from the places of their original anlage, continues to be under the nervous control of the cervical vertebrae.
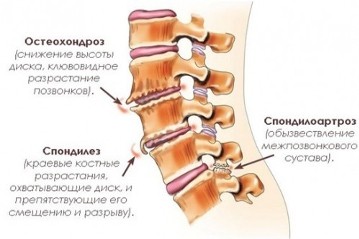
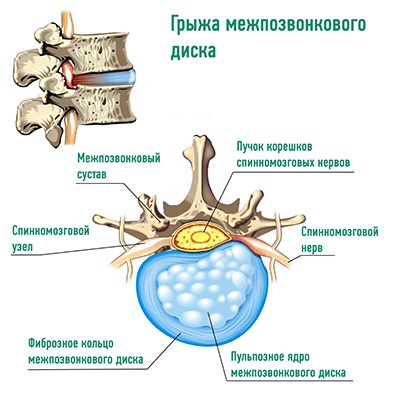
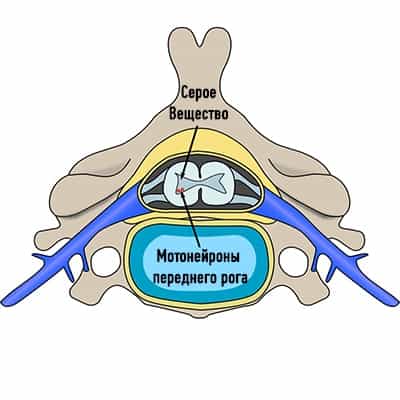
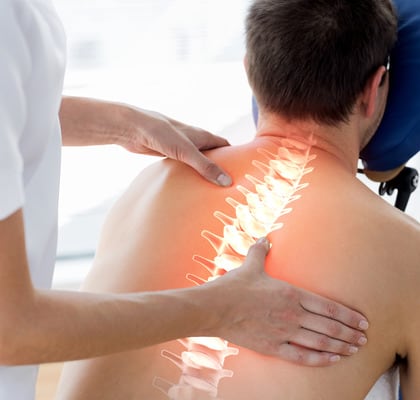
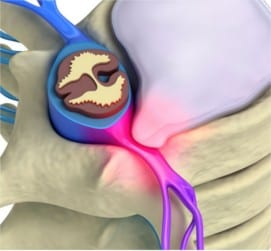
The spine, intercostal vessels and nerves meet the requirements of the metamery in full. The area of the spinal cord, spinal cord roots and spinal ganglia located in the foramens between the adjacent vertebrae are the leading metameric structure.
Each metamer consists of the seven tissues: ectoderm – dermatome (skin and its derivatives), neurotome (nervous system); mesoderm – vasotome (arterial, venous and lymphatic vessels), sclerotome (area of skeleton), myotome (skeletal and unstriated muscles); endoderm – enterotome (internal organs), glotome – (endocrine and immune systems).
Thus each neurotome in the human body has a clearly designated area of control (innervation) in all structures that forms this metamer.